
In this article, you’ll learn what is experiential learning and why it’s important for your learning progress.
Because of the continuously changing nature of the world we live in today, learning institutions must constantly integrate new learning techniques. Memorizing and repeating facts from a textbook won’t cut it in today’s learning environment. Students need to understand their learning materials by connecting closely with them ultimately. These new learning techniques will enable the students to be more hands-on and prepared for the future.
As opposed to didactic and routine learning techniques where the students play a passive role in their learning process, with new learning styles like experiential learning, the students have a more active role to play. Experiential learning keeps students curious and enthusiastic. It also enables people to learn in a way that suits their individual needs. This article will discuss what it is, how it works, its benefits, and others. So, let’s get right to it.
The foundation of experiential learning is to learn by doing – it is the process of learning through different experiences. It considers the role that experiences combined with emotions and environmental factors play in learning. When students are engaged in hands-on experiences, they can connect the theories learned to real-life situations. There are different forms of experiential learning opportunities, from community service to undergraduate research, internships, study abroad, field exercises, externships, laboratory experiments, practicums, and others.
Experiential learning also requires the students to be curious and self-motivated. Some of the elements this learning technique must include are as follows:
This term, Experiential Learning, was initially proposed by psychologist David Kolb in 1984, who emphasized the importance of experiences to the learning process.
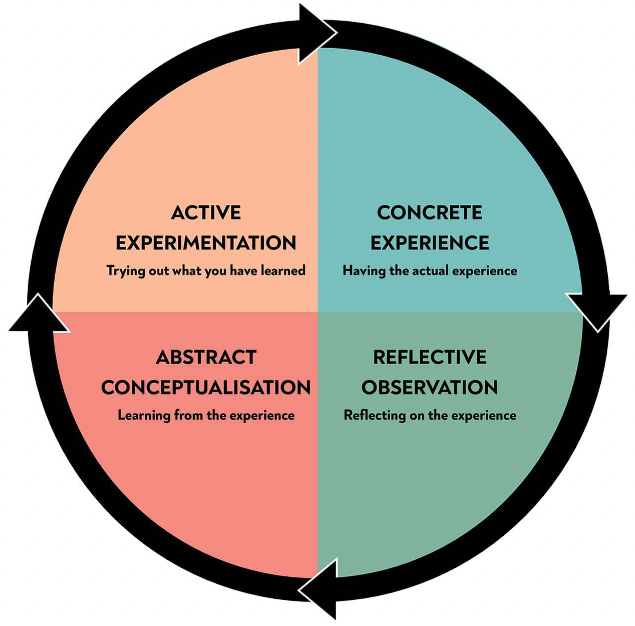
David Kolb’s experiential learning theory proposed that the experiential learning process is an integration of knowledge, activity, and reflection. He suggested that there is a consistent cycle that many students follow, which birthed the four major stages of the experiential learning cycle. Plus, many people participate in this experiential learning cycle without being aware.
Kolb’s Cycle of Experiential Learning

This is the first stage of the experiential learning cycle, and it involves participating actively in a learning experience. The experience can either be a new one or a familiar/past one in a new way. An example of a concrete experience includes learning to play a new instrument, going on a field trip for the first time, or learning to ride a bike. According to David Kolb, these concrete experiences offer the information needed as the foundation for reflection.
This cycle stage involves the student spending some time reflecting on the experience and assimilating the information gathered through the concrete experience.
After reflecting on the concrete experience, the next step is for the student to develop a theory or a model from their knowledge and reflections. This stage will involve them thinking about their next steps, developing a plan, or disclosing plans to an expert.
The final stage of the cycle involves acting on the theory or model formed after reflection and conceptualization, and it is referred to as active experimentation. In this stage, the student will apply what they learned in all the previous steps and see if there are any modifications when they try the experience again. Besides, this stage can either occur over a short or long time.
Individuals navigate the learning cycle due to different factors, like culture, personality, profession, education, and others. Kolb suggests that we as individuals lead with one of the learning styles and sometimes default to it when we are under stress. For example, some students will be more dominant in reflective observation and concrete learning, while others will be dominant in active experimentation and abstract conceptualization. The Kolb Experiential Learning Profile outlines nine different learning styles that people use to navigate the learning cycle. Highlighted below are some of these different experiential learning styles.
The experiencing style involves finding meaning in experiences and relationships – therefore, you are comfortable with teamwork and forming relationships with others. Also, learners that use this style are connected, involved, intuitive, and warm.
Learners that use the imagining learning style majorly learn from observations and reflections and tend to be compassionate, inventive, trusting, kind, and self-aware. This learning style also involves individuals that are comfortable with helping others, generating new ideas, and coming out of uncertain situations.
The reflecting learning style involves being careful, easy-going and reserved, and it means that you prefer to gather multiple perspectives and observe others before acting. Besides, learners that use this learning style allow others to take centre stage while they lay back and watch.
Learners that use the analysing learning style are disciplined, structured, and detailed, and it means that they like to think critically and methodically about their experiences before making plans. Additionally, you like to plan ahead to reduce mistakes and are methodical when analyzing data.
The thinking style involves being linear, organised, precise, and sceptical, and here, learners use quantitative tools, reasoning, and logic to analyse problems and frame arguments. Plus, with this style, you know how to make independent decisions and efficiently exchange ideas.
When learners use the deciding style, they are responsible, unswerving, and realistic and find practical solutions to different problems. This learning style enables you to be committed to one goal while working on the plan and evaluation as you go.
This learning style involves being confident and committed to different objectives and goals while being very time-conscious and achievement-oriented. Besides, regardless of limited resources, you can still execute plans.
This initiating learning style involves thinking on your feet and having an impulsive mindset, meaning that you take risks when looking for new openings. Learners with this learning style are able to shrug off losses and have the ability to try again despite failures.
The balancing style enables learners to identify blind spots, bridge the difference between people, and help team members quickly adapt to any situation. This means that you can adapt to ever-changing priorities with this learning style.
There are different forms of experiential learning. Some of the places you can apply experiential learning are outlined below.
Experiential learning has multiple benefits that are highlighted below:
Experiential learning enables learners to understand concepts better and apply them to real-world situations. As stated earlier, this learning technique allows users to play a more active role in their learning.
Experiential learning enables students to be more creative and innovative as they will use their knowledge and experiences to test their different theories. It also allows them to use distinct solutions to solve different challenges.
Experiential learning requires a more hands-on approach, enabling learners to take risks and make mistakes. This way, they can learn valuable lessons from their stakes, failures, and successes.
Reflection is an essential aspect of experiential learning, as it allows for learners to reflect on their experiences and develop concepts and theories to help them in different situations.
Experiential learning gives students a better attitude towards learning and improving their skills and knowledge.
Experiential learning styles enable students to change their mindset and prepare them for other future experiences.
As an instructor, you must use self-reflection, self-discovery, teamwork, problem-solving, and support to challenge students. Plus, you are responsible for what students will learn from their experiences. Outlined below are some factors to consider when integrating experiential learning into teaching.
There are different ways to find an experiential learning program as a student, and a number of them are outlined below:
The experiential learning process involves acquiring and applying knowledge learnt to real-life experiences. You can achieve this in different ways, from internships to volunteering, returnships, field trips, apprenticeship, fellowships, classroom activities, clinical education, and postgraduate programs. This learning technique has multiple benefits as it enables learners to learn from their mistakes, synthesize new information, work as a team, and reflect more.